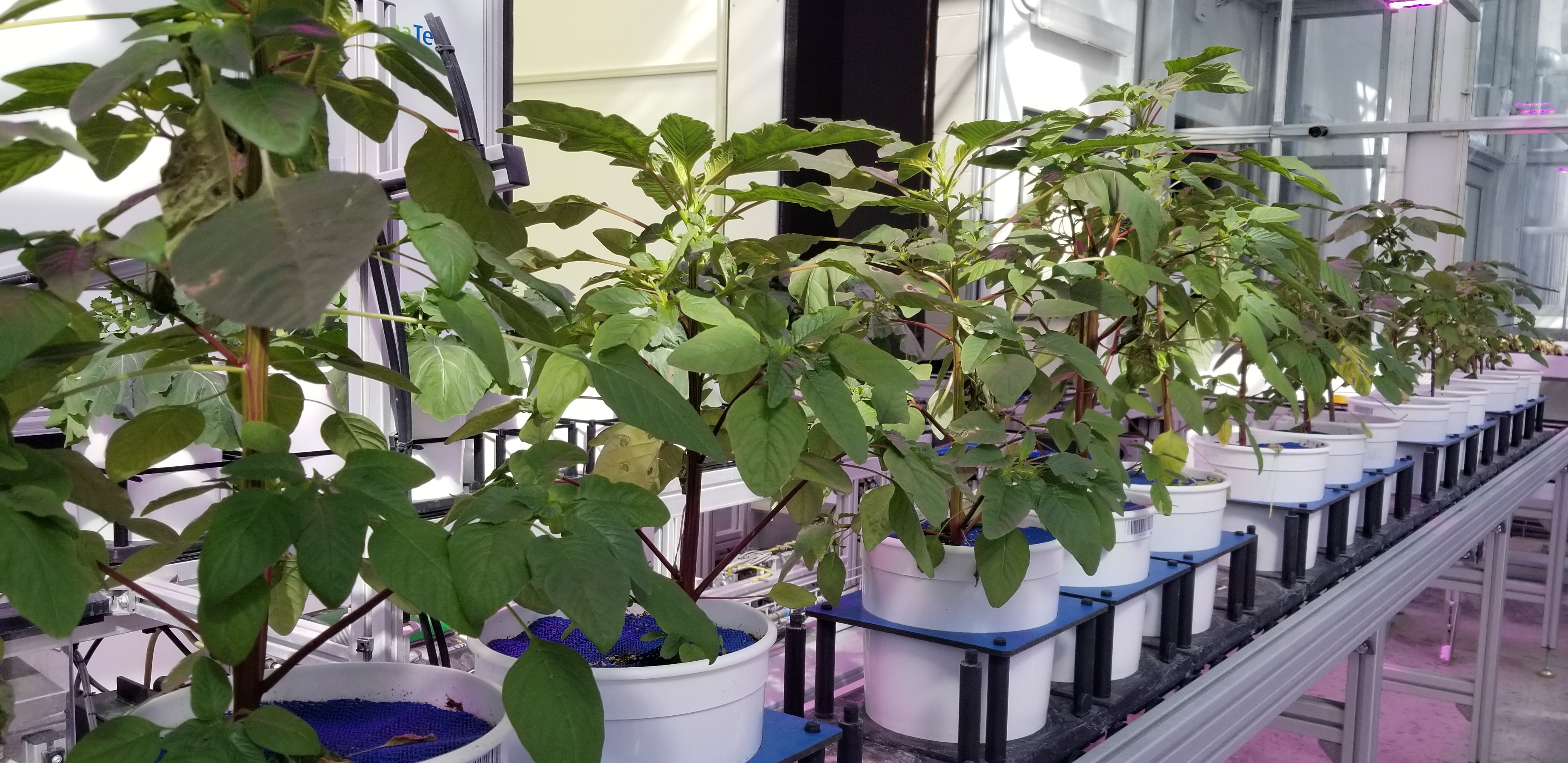
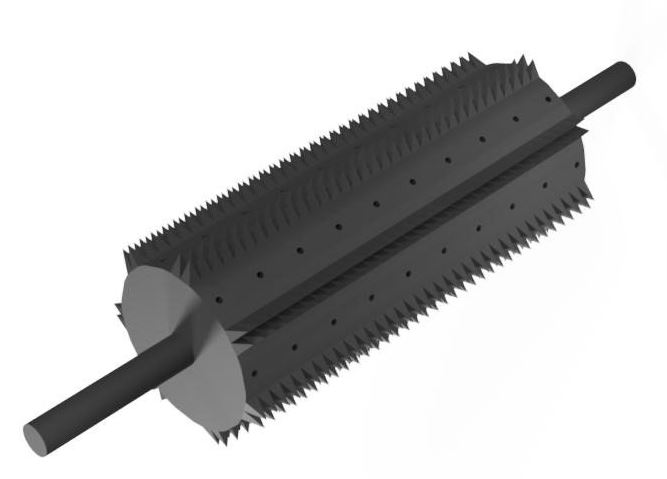
An increasing concern with today's agriculture is the rising amounts of chemicals introduced in the food chain. The introduction of Amaranthus palmeri (commonly known as palmer amaranth) has heightened awareness for alternative methods of eradicating crop invading weeds. It has become herbicide resistant and steels nutrients from crops creating yeild losses and ruining farming equipment. The Viljoen lab has developed an implement that injures the epidermis of the plant to more efficiently transport the herbicide to the plant.
Our technique uses this novel implement to apply herbicide with a sticking agent to treat the resistant weeds between rows of crops. Preliminary experiments show its efficacy, as seen below in the comparison videos. The first video shows traditional spray application of herbicides in the following order: control (water), glyphosate, dicamba, and 2,4-D with glyphosate.
This second video shows treatment with our novel applicator with herbicides in the following order: control (water), glyphosate, dicamba, and 2,4-D with glyphosate.
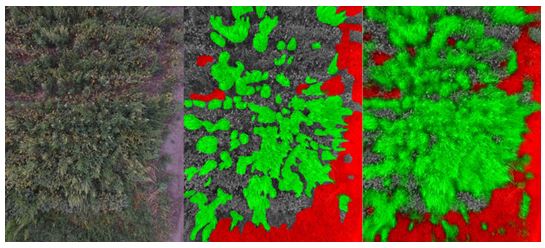
This novel applicator is part of a project with Eric Psota and Yeyin Shi using unmanned aircraft systems (UAS), and deep learning. The UAS takes images of a field, and the deep learning differentiates between what are crops, dirt, and undesireable weeds. To train the deep learning software, images were first hand annotated. The figure below shows from left to right: the UAS image, the hand annotated image, and the image produced from the deep learning software.